Introduction to Loxapine and Parkinson's Disease Psychosis
As a blogger who is passionate about mental health and neurological disorders, I've become increasingly interested in exploring the potential treatment options available for psychosis in Parkinson's disease. One such option that I recently came across is Loxapine, and in this article, I will be delving deeper into its potential as a treatment for psychosis in Parkinson's disease patients.
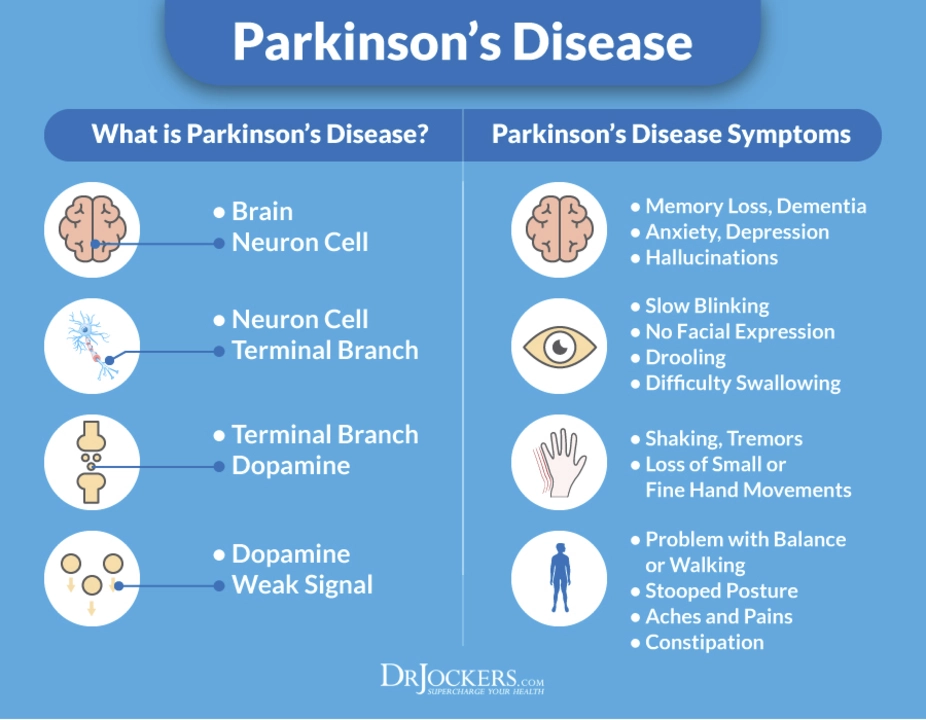
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement and can cause a range of other symptoms, including cognitive and emotional changes. In some cases, these changes can lead to the development of psychosis, which can have a profound impact on the individual's quality of life. Although there are several medications available to help manage Parkinson's disease, treating psychosis in these patients can be challenging.
What is Loxapine?
Loxapine is an antipsychotic medication that has been used for many years to treat schizophrenia. It belongs to a class of drugs known as typical antipsychotics and works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin. Loxapine is available in various forms, including oral tablets and an inhalable powder, making it a versatile treatment option for a range of psychiatric conditions.
Given its long history of use in managing schizophrenia, researchers have begun to investigate the potential of Loxapine in treating psychosis in Parkinson's disease patients. Although it may not be the first-line treatment for everyone, it could provide a valuable alternative for those who do not respond well to other medications or experience significant side effects.
Understanding Psychosis in Parkinson's Disease
Psychosis is a mental health condition characterized by a loss of contact with reality. People experiencing psychosis may have hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thinking, and these symptoms can be understandably distressing for both the individual and their loved ones. In Parkinson's disease, psychosis is thought to be related to the complex interactions between the underlying neurodegeneration and the medications used to manage the motor symptoms of the disorder.
It is estimated that up to 40% of people with Parkinson's disease will experience some form of psychosis during their illness. This can range from mild hallucinations to more severe delusions and paranoia. Psychosis in Parkinson's disease not only impacts the individual's quality of life but can also present significant challenges for caregivers and healthcare providers.
How Loxapine May Help Manage Psychosis in Parkinson's Disease
Loxapine's potential for managing psychosis in Parkinson's disease is thought to be related to its effects on dopamine and serotonin levels in the brain. By helping to regulate the balance of these neurotransmitters, Loxapine may help to reduce the severity and frequency of psychotic symptoms in some patients.
It is worth noting that Loxapine is not currently approved by the FDA for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease. However, several small studies and case reports have suggested that it may be beneficial in managing these symptoms in some patients. As such, it may be considered as an off-label treatment option by healthcare providers in certain cases.
Benefits of Loxapine in Parkinson's Disease Psychosis
One of the main benefits of Loxapine in treating psychosis in Parkinson's disease is its relatively low risk of worsening the motor symptoms of the disorder. Many antipsychotic medications can have a negative impact on movement and coordination, which can be particularly problematic for individuals with Parkinson's disease. However, Loxapine appears to have a lower risk of causing these issues compared to other antipsychotics.
Additionally, Loxapine's availability in both oral and inhalable forms may provide added convenience and flexibility for patients and healthcare providers. This could be particularly beneficial for those who have difficulty swallowing or require rapid relief from acute psychotic symptoms.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Loxapine
As with any medication, Loxapine is not without its potential risks and side effects. Some of the most common side effects associated with Loxapine include drowsiness, dizziness, and dry mouth. In rare cases, Loxapine can cause more serious side effects, such as severe muscle stiffness, high fever, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a potentially life-threatening reaction to antipsychotic medications).
It is also essential to consider the potential for drug interactions when using Loxapine in combination with other medications commonly prescribed for Parkinson's disease. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medications, and be sure to discuss any concerns or potential side effects you may be experiencing.
Discussing Loxapine with Your Healthcare Provider
If you or a loved one with Parkinson's disease is experiencing psychosis and you are interested in exploring the potential of Loxapine as a treatment option, it is crucial to discuss this with a healthcare provider. They will be able to provide a thorough evaluation of the individual's symptoms, medical history, and current medications to determine if Loxapine may be an appropriate and safe treatment choice.
It is essential to remember that each person's experience with Parkinson's disease and psychosis is unique, and what works for one individual may not be the best option for another. A healthcare provider will be able to guide you through the decision-making process and help you find the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs.
Conclusion: Loxapine as a Potential Treatment Option for Psychosis in Parkinson's Disease
In conclusion, Loxapine appears to hold promise as a potential treatment option for psychosis in Parkinson's disease. Its relatively low risk of worsening motor symptoms and its versatility in administration methods make it an intriguing option for patients and healthcare providers alike. However, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the possible risks and side effects associated with Loxapine and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider before beginning treatment.
As research into Loxapine and other treatment options for psychosis in Parkinson's disease continues, we can remain hopeful that more effective and targeted therapies will become available to improve the quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.

Kelly Thomas
April 30, 2023 AT 00:40Wow, this deep dive into loxapine and Parkinson's psychosis is like a breath of fresh air for anyone grappling with the maze of treatment options. You’ve painted the picture with such vivid clarity, making the pharmacology feel almost tangible. I especially love how you highlighted the lower risk of motor symptom exacerbation – that’s the golden thread many patients cling to. Your balanced view of off‑label use and the need for clinician oversight rings true like a well‑tuned bell. For caregivers, this article is a bright lantern in a foggy night, offering both hope and caution. Keep sprinkling that colorful knowledge; it really helps demystify a tough topic.
Mary Ellen Grace
April 30, 2023 AT 01:46Thx for the info, super helpful!
Carl Watts
April 30, 2023 AT 03:26One might ponder the epistemic boundaries when we venture into repurposing antipsychotics for neurodegenerative sequelae. The dance between dopamine modulation and motor integrity is a delicate choreography. While loxapine offers a tantalizing promise, we must question the ontological weight of anecdotal reports. Empirical rigor remains the lighthouse guiding us through these stormy seas. Yet, the very act of questioning fuels the engine of scientific progress. Hence, the discourse must continue, ever vigilant, ever curious.
Brandon Leach
April 30, 2023 AT 05:23Sure, because we all love off‑label meds. Works great, right?
Alison Poteracke
April 30, 2023 AT 06:46Your explanation is easy to follow and very kind. I think many patients will feel more at ease. It’s good to remind them to talk with their doctor. Thanks for the simple guidance.
Marianne Wilson
April 30, 2023 AT 08:26While the article is well‑intentioned, it borders on reckless optimism. Loxapine remains an off‑label choice without robust, randomized controlled trials to substantiate its safety profile in Parkinson’s psychosis. The modest side‑effect discussion glosses over the serious risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a condition that can be fatal if not promptly recognized. Moreover, the claim of "relatively low risk of worsening motor symptoms" contradicts the pharmacodynamic reality that typical antipsychotics, including loxapine, possess notable D2 antagonism, which can exacerbate bradykinesia. The piece also fails to address the possibility of drug–drug interactions, especially with levodopa, which can lead to unpredictable plasma concentrations and heightened dyskinesia. Patients and caregivers deserve a more nuanced appraisal, including the latest meta‑analyses that suggest limited efficacy compared to newer atypical agents. Additionally, the article neglects the FDA’s current stance, which may influence insurance coverage and accessibility, thereby imposing an additional financial burden on already strained families. The tone of enthusiasm may inadvertently pressure clinicians to prescribe without thorough deliberation, undermining the principle of informed consent. It is also worth noting that inhalable loxapine, while convenient, may not be suitable for patients with compromised respiratory function-a common comorbidity in advanced Parkinson’s disease. The omission of these critical considerations reduces the article to a promotional overview rather than an evidence‑based resource. In summary, the discussion should be anchored in rigorous data, explicit risk‑benefit analysis, and transparent acknowledgment of regulatory limitations.
Patricia Bokern
April 30, 2023 AT 10:06Hold on, did anyone notice how pharma never tells you about the hidden agendas? They want us to chase every new off‑label hype while they keep the real cures under lock and key. This whole loxapine talk feels like a distraction from the big picture-are they hiding something? It’s like they’re feeding us snake oil dressed up as a miracle.
Garrett Gonzales
April 30, 2023 AT 11:46From a neuropharmacological perspective, loxapine’s affinity for D2 and 5‑HT2A receptors suggests a complex modulatory effect on the mesocorticolimbic pathway, which could theoretically mitigate hallucinations without severely dampening nigrostriatal dopamine transmission. However, the receptor occupancy data are still sparse in the PD cohort, and the PK/PD variability raises concerns about dose titration. Clinicians should leverage therapeutic drug monitoring and consider adjunctive use of pimavanserin as a comparative benchmark. Ultimately, integrating real‑world evidence with mechanistic modeling will be essential to delineate loxapine’s niche within the PD psychosis treatment algorithm.