Betamethasone Relief Time Calculator
Quick Take
- Betamethasone usually begins reducing redness and itching within 24-48hours for most acute skin flares.
- Full improvement can take 3‑7days, depending on potency, condition type, and skin thickness.
- Occlusive dressings or higher‑strength formulations may cut the onset time by half.
- Side‑effects such as skin thinning become more likely after two weeks of continuous use.
Betamethasone is a synthetic potent glucocorticoid used in topical form to calm inflammation, itch, and immune reactions in the skin. Its chemical structure, a fluorinated corticosteroid, gives it a high affinity for the glucocorticoid receptor, which translates into strong anti‑inflammatory power at low concentrations.
How Topical Corticosteroids Calm the Skin
When you apply a steroid cream, the active molecule must first penetrate the stratum corneum. Once inside, it binds to intracellular glucocorticoid receptors, migrates to the nucleus, and switches off genes that produce inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and cytokines. This cascade reduces swelling, redness, and the sensation of itch.
Inflammation is the body's immune response to injury or irritation, characterized by heat, redness, swelling, and pain. In skin disorders, chronic inflammation drives the persistent lesions seen in eczema and psoriasis.
Typical Onset of Action for Betamethasone
Clinical observations and trial data show a fairly predictable timeline:
- 0-12hours: The drug begins to absorb; patients may notice a subtle reduction in burning or stinging.
- 12-48hours: Visible decrease in erythema (redness) for acute flares of Eczema (atopic dermatitis), especially on thin skin areas like the face or flexural folds.
- 48hours-3days: Itch intensity drops significantly; plaques start to flatten.
- 3-7days: Most patients see near‑complete resolution of mild‑to‑moderate lesions. For thicker plaques, such as those in Psoriasis, full clearance may take up to two weeks.
These windows assume consistent twice‑daily application to clean, dry skin.
Factors That Speed Up or Slow Down Relief
Not every skin surface reacts the same way. Several variables shift the clock:
- Potency class: Betamethasone is a ClassII (high‑potency) steroid. Compared with low‑potency agents like Hydrocortisone, it reaches therapeutic levels faster.
- Formulation type: Creams and ointments differ in base composition. Ointments generally enhance penetration, cutting onset time by ~20%.
- Skin thickness: Thin areas (eyelids, genitalia) absorb quicker than calloused sites (palms, soles).
- Occlusion: Covering the treated area with a breathable bandage traps moisture, boosting absorption and often delivering relief within half the usual time.
- Severity and chronicity: Acute flare‑ups respond faster; long‑standing plaques may need a loading phase of 5‑7days before noticeable change.
Comparing Betamethasone with Other Topical Steroids
| Steroid | Potency Class | Typical Concentration | Average Onset (Redness Reduction) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betamethasone | II (High) | 0.05% (cream/ointment) | 12-48hrs |
| Hydrocortisone | VII (Low) | 1% (cream) | 48-72hrs |
| Clobetasol | I (Super‑high) | 0.05% (gel/cream) | 8-24hrs |
While clobetasol may act faster, its super‑high potency makes it unsuitable for long‑term use on delicate skin. Betamethasone hits a sweet spot: quick relief without the aggressive side‑effect profile of ClassI agents.
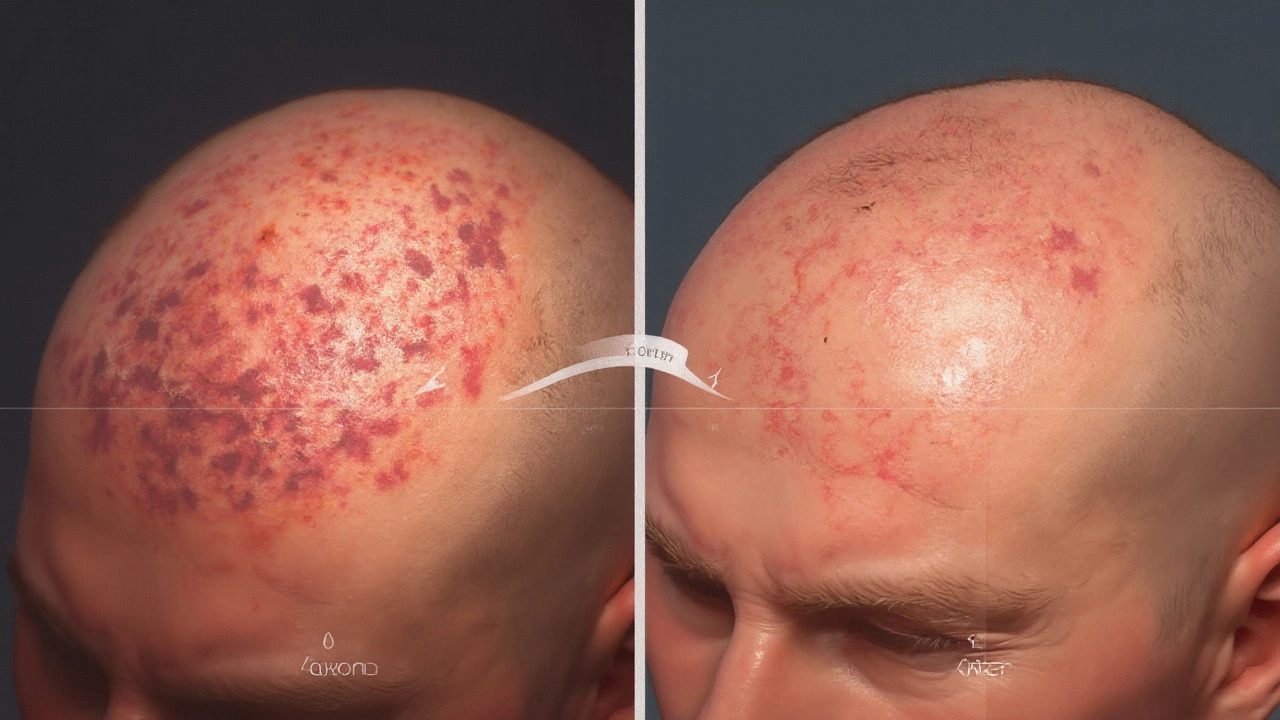
Real‑World Expectations for Common Conditions
Below is a quick guide on when patients typically notice improvement.
| Condition | Typical Onset with Betamethasone | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Eczema (atopic dermatitis) | 24-48hrs for itch reduction; 3-5days for lesion flattening | Best on flexural sites; avoid prolonged use on face. |
| Psoriasis plaques | 3-7days for noticeable scaling down; up to 14days for thick plaques | Combine with a keratolytic (e.g., salicylic acid) for faster results. |
| Contact dermatitis | 12-24hrs for erythema improvement | Identify and remove the irritant; steroid accelerates recovery. |
| Lupus erythematosus (discoid) | 4-6days for lesion lightening | Often paired with antimalarial therapy for systemic control. |
Balancing Speed with Safety
Quick relief is attractive, but it shouldn't come at the cost of skin health. Key safety points:
- Duration limit: For most body sites, limit continuous use to 2‑4weeks. Extend only under specialist supervision.
- Side‑effects: Skin thinning, telangiectasia, and steroid‑induced acne can appear after 2weeks of daily use.
- Tapering: When discontinuing after longer courses, gradually reduce frequency to avoid rebound inflammation.
- Regulatory guidance: Both the FDA and WHO recommend using the lowest effective potency for the shortest necessary period.
Practical Tips for Faster Relief
- Cleanse the area gently; avoid soaps with high pH that strip natural lipids.
- Apply a thin veneer of betamethasone and let it absorb for 2-3minutes before covering.
- Consider an occlusive dressing for stubborn plaques, but limit to 12hours per day.
- Track symptom scores (e.g., itch VAS) daily; if no improvement after 72hours, reassess diagnosis.
- Combine with moisturizers that contain ceramides to restore barrier function and reduce steroid dependence.
When to Seek Professional Help
If after a week there’s no visible improvement, or if the rash spreads, becomes pustular, or you notice new side‑effects, schedule a visit. Dermatologists may add a short‑course systemic steroid or switch to a different topical class.
Frequently Asked Questions
How soon can I expect the itching to stop?
Most patients notice a reduction in itch within the first 12-24hours of twice‑daily application. Full relief generally follows by the third day.
Can I use betamethasone on my face?
Yes, but only for short periods (max 2weeks) and at the lowest effective concentration. The facial skin is thin, so side‑effects like skin thinning appear faster.
Is it safe to combine betamethasone with other skin products?
Moisturizers, barrier‑repair creams, and non‑oil‑based sunscreens are generally safe. Avoid layering with other topical steroids or harsh exfoliants, which can increase irritation.
What should I do if my rash worsens after starting treatment?
Stop the medication and contact a healthcare professional. Worsening may signal infection, an allergic reaction, or an incorrect diagnosis.
How does betamethasone compare to over‑the‑counter hydrocortisone?
Betamethasone is roughly 30‑50times more potent than 1% hydrocortisone, leading to faster symptom control, especially for moderate‑to‑severe inflammation.


Iain Clarke
September 23, 2025 AT 15:05Betamethasone typically starts to calm redness within the first day, especially on thinner skin such as the face or flexural areas. By the second day you’ll often notice the itching easing, and most patients see a respectable improvement by day three or four. Consistent twice‑daily application and a clean skin surface are key to achieving this timeline. Keep an eye on the duration of use; two to four weeks is generally advised to minimise side‑effects.
Courtney Payton
September 30, 2025 AT 05:12One must consider the ethical implication of applying a potent steroid without due caution; it is not merely a cosmetic choice. The temptation to over‑use betamethasone defnitely conflicts with the principle of "do no harm". While the article offers useful data, it glosses over the moral responsibility of monitoring for skin atrophy. A patient should be educated about the risk, lest the short‑term relief become a long‑term burden.
Muthukumaran Ramalingam
October 6, 2025 AT 19:19So, you slap the cream on, right? First thing, the skin kinda drinks it up in a few hours, you’ll feel that the burn or sting is fading. Then, after about a day, the red patches start to look less angry. By the time you hit the 48‑hour mark, the itch is usually a lot less annoying. If you keep doing the twice‑daily routine, you’ll see the plaques flatten out over a few days. Thick spots like on the palms might need a week or so, but most of the time you’ll be happy with the change. Just don’t forget to wash your hands before you put it on, otherwise you’ll spread the drug to places you don’t want it.
Garrett Williams
October 13, 2025 AT 09:26Betamethasone works fast if you use it right.
joba alex
October 19, 2025 AT 23:33While the consensus leans on the 12‑48 hour window, the pharmacokinetic profile suggests that barrier integrity and occlusive variables can shift the onset by an order of magnitude; in other words, you might see negligible effect for up to 72 hours if the vehicle is suboptimal. Moreover, the term “rapid relief” is deceptive without context-clinical endpoints vary wildly between atopic dermatitis and discoid lupus, rendering a one‑size‑fits‑all timeline scientifically untenable.
Rene Lacey
October 26, 2025 AT 12:40When we examine the kinetic cascade of betamethasone absorption, we must first acknowledge the role of the stratum corneum as a selective filter, permitting only a fraction of the applied dose to reach viable epidermis. The initial 0‑12 hour phase is marked by molecular diffusion, during which patients often report a subtle decrease in burning sensations. By the twelve‑to‑forty‑eight hour interval, the glucocorticoid receptors become sufficiently occupied to suppress pro‑inflammatory cytokine transcription, leading to visible macular attenuation. This manifests clinically as a perceptible fading of erythema, especially on thin skin regions. As the thirty‑to‑seventy‑two hour window progresses, the anti‑pruritic effect becomes more pronounced, with many users noting a marked decline in itch intensity. The subsequent seventy‑two‑hour to three‑day phase sees the remodeling of papillary architecture, resulting in the flattening of plaques. For conditions such as psoriasis, this structural reorganization may require an additional week for complete clearance, given the hyperkeratotic nature of lesions. Occlusion, when applied judiciously, can halve these temporal milestones by enhancing hydration and drug solubility. Conversely, neglecting proper skin preparation-such as using harsh soaps-can delay onset by up to 50 percent. It is also essential to consider patient adherence; inconsistent application inevitably prolongs the therapeutic timeline. Importantly, the risk of cutaneous atrophy escalates after two weeks of uninterrupted use, underscoring the need for treatment holidays. Therefore, clinicians often advise a tapering schedule after the initial improvement phase. Monitoring tools, such as visual analogue scales for itch, can provide objective feedback on efficacy. Should no appreciable change be observed after seventy‑two hours, a reassessment of diagnosis or potency may be warranted. Finally, integrating moisturizers that restore barrier function can synergize with betamethasone, accelerating both relief and long‑term skin health.
johnson mose
November 2, 2025 AT 02:48Imagine a storm of inflammation being tamed by a gentle breeze-that's betamethasone in action. The cream slides across the skin like a silk tapestry, delivering its potent message to the cellular choir. Within a day, the angry red chorus begins to quiet, and the relentless itch loses its voice. For thick, stubborn plaques, think of it as a slow sunrise: the light gradually seeps in, eroding the darkness. Pair it with a nourishing moisturizer and you’ll witness a transformation that feels almost cinematic.
Charmaine De Castro
November 8, 2025 AT 16:55Betamethasone is a solid choice when you need faster relief than hydrocortisone can offer. Apply a thin layer twice daily to clean, dry skin, and you should notice the itching subside within the first 24 hours. For facial areas, limit use to two weeks to avoid thinning. Remember to keep your skin moisturized to support the barrier while the steroid does its work.
Mark Mendoza
November 15, 2025 AT 07:02💡Quick tip: use betamethasone on a clean surface and give it a minute to absorb before you slap on any occlusive dressing. ⏱️You’ll typically see the redness start to fade after about 12‑48 hours. 📅If nothing changes after three days, it might be time to revisit your diagnosis with a dermatologist.
Dan Tourangeau
November 21, 2025 AT 21:09Apply betamethasone twice daily to the affected area; improvement usually begins within 24 hours. Limit continuous use to four weeks to reduce thinning risk. Moisturize after each application to maintain barrier function.
Bernard Valentinetti
November 28, 2025 AT 11:16- In the grand tapestry of cutaneous pharmacology, betamethasone occupies a pre‑eminent niche; its molecular affinity for glucocorticoid receptors renders it a veritable maestro of anti‑inflammatory symphonies. - Consequently, one observes a diminution of erythema within a temporal window of approximately twelve to forty‑eight hours; a period that, while seemingly brief, is underpinned by intricate intracellular cascades. - Nonetheless, the practitioner must remain vigilant, for prolonged exposure begets dermal atrophy-a fate most undesirable. - 🧪Hence, judicious application coupled with strategic occlusion can halve this interval, delivering relief with alacrity. - 🕒In sum, the balance of potency and prudence dictates optimal outcomes.
Kenneth Obukwelu
December 5, 2025 AT 01:23Betamethasone, in its potent elegance, reminds us that relief is not instant but earned through disciplined application. The skin, a resilient canvas, accepts the steroid’s counsel, and in turn, the inflammation bows. When wielded responsibly, the onset of calm can be felt within a single day, a testament to the harmony of science and care.
Josephine hellen
December 11, 2025 AT 15:30Hey there, fellow skin‑warrior! I know it can feel like you’re stuck in a never‑ending loop of itch and flare, but betamethasone is like that reliable friend who shows up right when you need them most. Start by cleaning the area gently-no harsh soaps-then spread a thin layer of the cream twice a day. Within the first 24 hours you’ll likely notice the burning sense start to ease, and by the second day the redness should look less aggressive. Keep the routine going, and by the fifth day most of the lesions will have softened considerably. Just remember, the skin is a living organ, so after a couple of weeks you’ll want to give it a break to avoid thinning. If you ever feel the rash isn’t improving, don’t panic-reach out to a dermatologist who can tweak your regimen. Stay positive, stay consistent, and the skin will thank you.
Ria M
December 18, 2025 AT 05:37Behold the marvel of dermatologic alchemy! Betamethasone descends upon inflamed dermis like a herald of calm, silencing the angry cytokines that have long held court. Within a mere half‑day, the prickling sensation begins its retreat, and by the close of the second day the crimson veil lifts ever so slightly. Yet, patience is the virtue required; for the most stubborn plaques, the full transformation may span a week or more. Thus, the saga of relief is both swift and measured, a delicate dance between potency and perseverance.
Michelle Tran
December 24, 2025 AT 19:44Betamethasone works fine, but honestly, the hype is a bit over the top. 🙄 It’ll chill the itch in a day or two, no big deal. Just don’t overdo it or your skin will get thin.
Caleb Ferguson
December 31, 2025 AT 09:51When using betamethasone, apply a pea‑sized amount to the affected zone and massage gently until absorbed. Expect noticeable reduction in redness after the first 24 hours, with itch diminishing shortly thereafter. Limit continuous use to a maximum of four weeks, and follow with a barrier‑restoring moisturizer.
Delilah Jones
January 6, 2026 AT 23:58Betamethasone can speed up relief, but only if you stick to the schedule. Missed doses will push the timeline back, so be consistent. If you see no change after three days, consider a different approach.
Pastor Ken Kook
January 13, 2026 AT 14:05Got the cream on? Good. 👍 Give it a few hours, then check the spot-most people see the redness start to fade around the 12‑hour mark. If you’ve been diligent twice a day, by day two the itch should be way down. Keep the routine, stay chill, and you’ll be back to smooth skin soon! :)