Allergy Medication Comparison Tool
This tool helps you compare the top over-the-counter antihistamines based on your specific symptoms and lifestyle needs.
Your Allergy Profile
Seasonal sniffles and sneezing can ruin a day, but you don’t have to settle for the first pill you find. If you’ve ever wondered whether Claritin really outperforms the competition or if another brand might suit you better, you’re in the right place. This guide breaks down the most common over‑the‑counter antihistamines, showing where each shines and where they fall short.
How Antihistamines Tame Your Symptoms
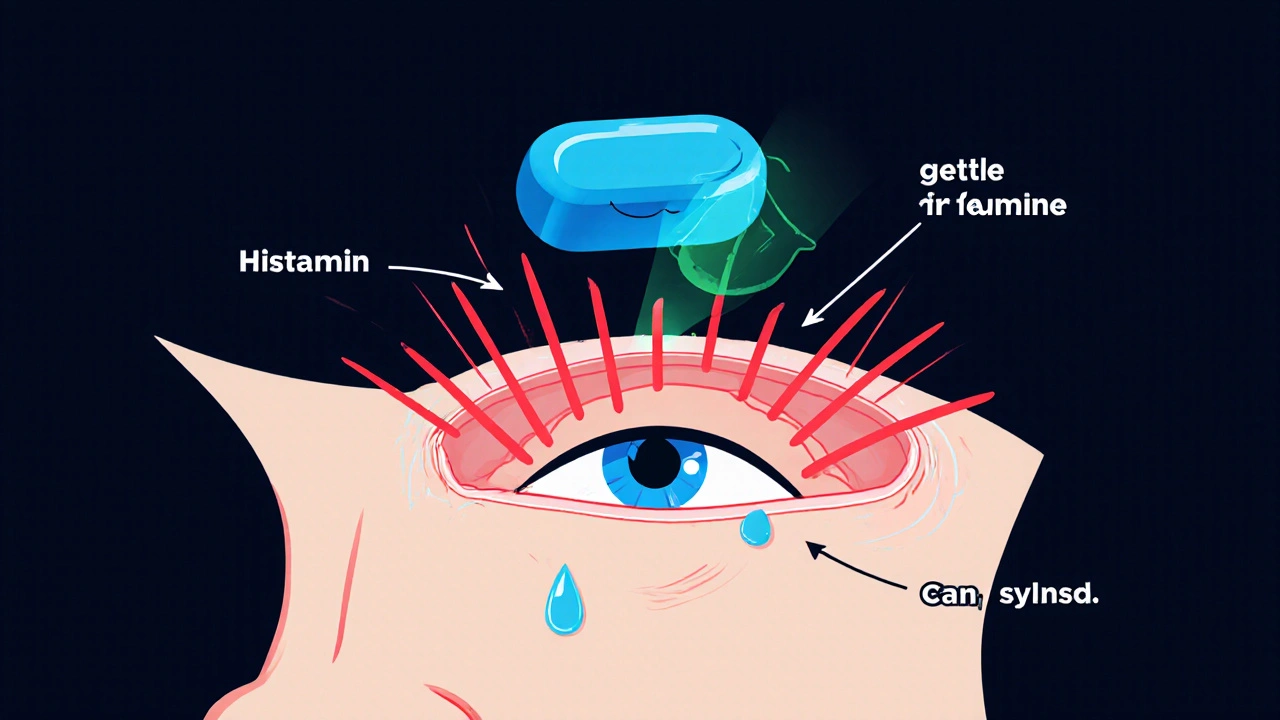
Allergy medicines belong to the antihistamine class. When you inhale pollen or pet dander, your body releases histamine. Histamine binds to receptors in the nose, eyes, and throat, causing itching, swelling, and mucus production. Antihistamines block those receptors, stopping the chain reaction before you feel the itch.
Claritin (Loratadine) - The Baseline
When it comes to seasonal allergies, Claritin (Loratadine) is a popular non‑sedating option. It earned FDA approval in 1993 and has stayed on the market ever since. Key attributes:
- Typical adult dose: 10mg once daily
- Onset of relief: 1-3hours
- Duration: Up to 24hours
- Side‑effects: Minimal drowsiness (≈2% of users)
- Price (US, 2025): $12 for a 30‑day supply (generic)
Because it doesn’t cross the blood‑brain barrier easily, most people can take Claritin without feeling sleepy, making it a go‑to for work or school.
Top Alternatives at a Glance
While Claritin works for many, three other OTC antihistamines often enter the conversation:
- Zyrtec (Cetirizine)
- Allegra (Fexofenadine)
- Xyzal (Levocetirizine)
Each has a slightly different potency, onset speed, and drowsiness profile. Below we dig into the details.
Detailed Profiles of the Alternatives
Zyrtec (Cetirizine) was FDA‑approved in 1995. It’s a second‑generation antihistamine like Loratadine but tends to act a bit faster.
- Adult dose: 10mg once daily (or 5mg for children 6‑11)
- Onset: 30‑60minutes
- Duration: 24hours
- Drowsiness: ~10% report mild sleepiness
- 2025 price: $10 for 30 tablets (generic)
Allegra (Fexofenadine) entered the market in 1996 and prides itself on being “non‑sedating”.
- Adult dose: 180mg once daily (or 60mg twice daily)
- Onset: 1hour
- Duration: Up to 24hours
- Drowsiness: <1% (practically none)
- 2025 price: $13 for 30 tablets (generic)
Xyzal (Levocetirizine) is the active enantiomer of cetirizine, launched in 2007. It aims for high potency with a low sedation rate.
- Adult dose: 5mg once daily
- Onset: 1hour
- Duration: 24hours
- Drowsiness: ~5%
- 2025 price: $15 for 30 tablets (generic)
Side‑by‑Side Comparison Table
| Medication | Active ingredient | Onset (min) | Typical dose | Drowsiness (% users) | Average price (30‑day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claritin | Loratadine | 60‑180 | 10mg QD | 2% | $12 |
| Zyrtec | Cetirizine | 30‑60 | 10mg QD | 10% | $10 |
| Allegra | Fexofenadine | 60‑120 | 180mg QD | 1% | $13 |
| Xyzal | Levocetirizine | 60‑120 | 5mg QD | 5% | $15 |
When Claritin Is the Right Choice
If you need a solid, non‑sedating pill that stays effective for a full day and you’re not overly price‑sensitive, Claritin is a safe bet. It’s especially handy for:
- All‑day office meetings or driving
- People who have tried Zyrtec and felt too sleepy
- Patients with mild to moderate hay fever who don’t need the ultra‑fast onset of Zyrtec
When an Alternative Might Edge Out Claritin
Consider Zyrtec if you’re racing against time-its 30‑minute kick can be a lifesaver during a sudden pollen spike. Alegra shines for those who *never* tolerate any drowsiness, even the low 2% reported with Claritin. Xyzal is a good middle ground: stronger than Claritin but still less sedating than Zyrtec for most users.

Safety, Interactions, and Practical Tips
All four drugs are generally safe, but keep these points in mind:
- Avoid combining with alcohol or other sedatives, especially with Zyrtec and Xyzal.
- Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a first‑generation antihistamine; it’s highly sedating and should be saved for occasional nighttime use.
- Pregnant or nursing moms should consult a doctor before starting any antihistamine.
- Most antihistamines can be taken with or without food, but a fatty meal may slightly delay absorption of Allegra.
A quick rule of thumb: if you notice any lingering fatigue, try switching from Zyrtec to Claritin or Allegra before adding a stimulant.
Quick Cheat Sheet
- Fastest onset: Zyrtec (30‑60min)
- Least drowsy: Allegra (<1%)
- Best all‑day non‑sedating: Claritin (2% drowsiness)
- High potency, moderate drowsiness: Xyzal (5%)
Bottom Line
There’s no one‑size‑fits‑all antihistamine. Claritin offers reliable, low‑sedation relief for most day‑long needs. Zyrtec wins on speed, Allegra on ultra‑low sedation, and Xyzal on a balance of potency and sleepiness. Evaluate your symptom timing, tolerance for drowsiness, and budget, then pick the pill that aligns with your lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take Claritin and Zyrtec together?
It’s not recommended. Both block the same histamine receptors, so using them together doesn’t boost effectiveness and can increase side‑effects, especially drowsiness.
Is Claritin safe for children?
Yes. The pediatric dose is 5mg once daily for kids 2‑5 years and 10mg for ages 6‑11. Always follow the label or a pediatrician’s guidance.
What’s the difference between Loratadine and Cetirizine chemically?
Loratadine is a p‑pyridine derivative, while cetirizine adds a chlorine atom that increases its affinity for the H1 receptor, leading to a faster onset but slightly higher sedation rates.
Can I use Allegra if I’m on blood‑pressure medication?
Generally yes. Allegra has minimal interaction with most antihypertensives, but always double‑check with your pharmacist, especially if you take a potassium‑sparing diuretic.
Why does Benadryl make me so sleepy?
Benadryl is a first‑generation antihistamine that crosses the blood‑brain barrier, directly affecting central nervous system receptors. That’s why it’s often used as a nighttime sleep aid.

Samantha Oldrid
October 17, 2025 AT 01:40Oh sure, because the government needed another excuse to push cheap pharma down our throats. Claritin? Just a glorified placebo dressed up in a fancy label. If you trust big‑co labs, you’ll believe any hype they sell. Wake up.
James Falcone
October 17, 2025 AT 02:46Look, we got enough of those foreign “miracle” pills already. Made‑in‑USA antihistamines are the real deal. Claritin’s just another product of our own brilliant industry. It works, no need to overcomplicate. Proud to support homegrown meds.
Frank Diaz
October 17, 2025 AT 03:53When we examine the phenomenon of allergy relief, we are confronted with the larger question of how humanity attempts to dominate its own biology. The modest tablet of loratadine becomes a symbol of the modern pact between nature and technology, a pact that promises comfort at the cost of surrendering agency. One could argue that each dose is a ritualistic acquiescence to the market’s narrative of control, a narrative that masks the underlying entropy of the immune system. Yet the data suggest that Claritin offers a predictable blockade of histamine receptors, a mechanistic clarity that many find reassuring. This predictability, however, masks the subtle influence of corporate interests that dictate dosage, branding, and distribution. Consider also the comparative pharmacodynamics of cetirizine and fexofenadine; they each present a nuanced variation on the same biochemical theme. The faster onset of Zyrtec, for instance, invites a different user experience, one that may align more closely with the urgency of modern life. Meanwhile, Allegra boasts a non‑sedating profile that appeals to the productivity‑driven individual. Each of these alternatives, while chemically distinct, ultimately converge on the same societal expectation: immediate relief without side‑effects. This expectation is itself a cultural construct, forged in an age where discomfort is deemed unacceptable. The ethical dimension of prescribing such medications without addressing root causes – environmental allergens, lifestyle, diet – remains largely unexamined. In the grand tapestry of health, antihistamines are but a thread, easily overlooked yet essential to the pattern. Their ubiquity invites complacency, a collective numbness to the deeper immunological dialogues. Therefore, while Claritin serves its purpose, it also perpetuates a cycle of temporary fixes. The wise consumer should remain skeptical of any product that promises convenience without fostering deeper understanding. Ultimately, the choice of antihistamine reflects a personal philosophy toward health: whether one seeks instant convenience or strives for holistic insight.
Tom Green
October 17, 2025 AT 05:00That was a deep dive, and I appreciate the broader perspective. It’s true that antihistamines are just one piece of the puzzle. Many folks benefit from pairing them with environmental controls, like air filters and regular cleaning. Understanding how each medication fits into that larger strategy can empower better choices. Keep exploring, and share what works for you.
Rebecca Mitchell
October 17, 2025 AT 06:06Claritin works but it’s not the only option
Lauren Sproule
October 17, 2025 AT 07:13yeah i get u sometimes the generic version is cheap n works fine but if u get drowsy try xyzal it might be the sweet spot for u
CHIRAG AGARWAL
October 17, 2025 AT 08:20Honestly i don’t care which one you pick as long as it stops the sneeze i just grab whatever’s on sale and move on
genevieve gaudet
October 17, 2025 AT 09:26in my view the act of selecting an antihistamine is a tiny reflection of how cultures negotiate the balance between nature and technology it’s fascinating how a simple pill can hold such symbolic weight across societies
Patricia Echegaray
October 17, 2025 AT 10:33Don’t you see the grand design? They want us divided over brand names while the shadow elites pull the strings. The “natural” vs “synthetic” war is a distraction to keep us from questioning the true agenda. Only the red‑white‑blue truth can cut through the haze. Stay vigilant, stay American.